Test of General Mental Ability (TGMA)
Overview
The Test of General Mental Abilities (TGMA) is almost always administered with the CNT. When ordering the two tests together, one might request the “contigma.” The TGMA is composed of five tests:

TABLE 7. THE TGMA
Many Ss score 0 on the VRT. This is odd, because the test is intuitive and is used by anthropologists to study IQ in primitive tribesmen.
WHAT DOES THE TGMA MEASURE?
Presumably, the TGMA measures general mental ability, or IQ. The vocabulary test of the WAIS and matric reasoning (the equivalent of the VRT) are the most highly g loaded subtests; the former is considered a test of crystallized intelligence and relates to verbal IQ; the latter is a test of fluid intelligence and relates to performance IQ. That is the theory, anyway.
We have been using the Vocabulary test for many years, first as a paper-and-pencil test with 40 items and three forms, currently with 21 items generated randomly but presented in order of difficulty. The vocabulary words towards the end of the test are extremely difficult; a high score indicates a particularly literate individual. By thew same token, the last few items on the VRT and EIT are extremely challenging. The original VT was only moderately correlated with FSIQ (r=0.44, P=0.002) but highly correlated with SAT verbal scores (r=0.72, P=0.002). The original VRT was the “non-verbal reasoning test” on CNS Vital Signs, but it was a timed test, while the VT, VRT and EIT are untimed.
RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE TESTS
Data from 418 Ss show that performance on the tests is interrelated. This is only to be expected: one of the best replicated findings in psychometrics is that, in the undamaged brain, performance on virtually any cognitive task correlates positively with performance on any other. Since the CNT is a measure of general mental ability and processing speed, then it should correlate with tests on the TGMA. Spearman’s theory is that complex problem-solving tasks necessarily share some specific information-processing resource (Spearman, 1927); Salthouse wrote that speed of processing is a fundamental part of the ”architecture of the cognitive system” as it develops across the lifespan (Kail & Salthouse, 1994)(Salthouse, 1996). Jensen is associated with a theory that complex reaction time measures are an index of the speed and efficiency with which the nervous system processes elementary information.
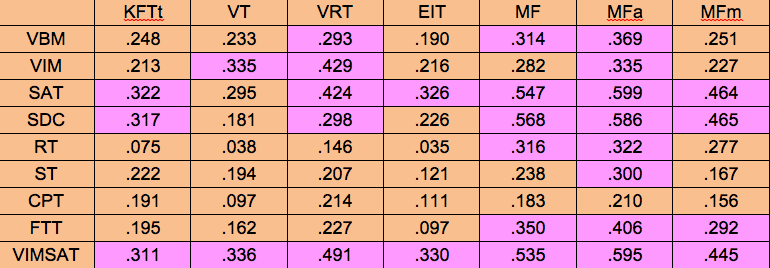
CORRELATIONS BETWEEN THE CNT AND TGMA
The VRT and MFa correlate best with the CNT. This suggests that they are measures of what psychologists call “fluid intelligence.” The VT, on the other hand, is the best correlated with age and education, and is an indicator of “crystallized intelligence.”
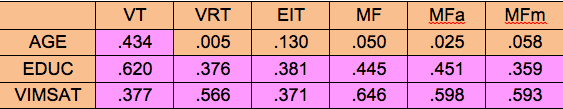
TABLE 9. THE TGMA, AGE AND EDUCATION AND THE VIMSATSCORE
The two tests in the CNT that are most highly correlated with FSIQ are the VIM and the SAT. Combining the two scores into VIMSAT, the correlation with FSIQ is 0.664, which is very high.
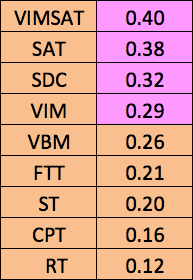
TABLE 9. THE TGMA, AGE AND EDUCATION AND THE VIMSATSCORE
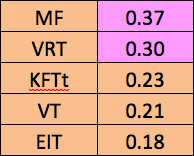
TABLE 11. AVERAGE TGMA CORRELATIONS WITH THE CNT
TGMA NORMS
Norms for the TGMA were derived from the NCNC DB of 6523 Ss age 4-94 as of 04.21.13. Zero scores were deleted. More highly educated Ss were deleted to match US Census average education level of 12.6 for adults. There were more males (2009 vs 1684). Blacks were over-represented (18%), hispanics under-represented (4%). Whites, Asians and Native Americans were proportionate to the US population.
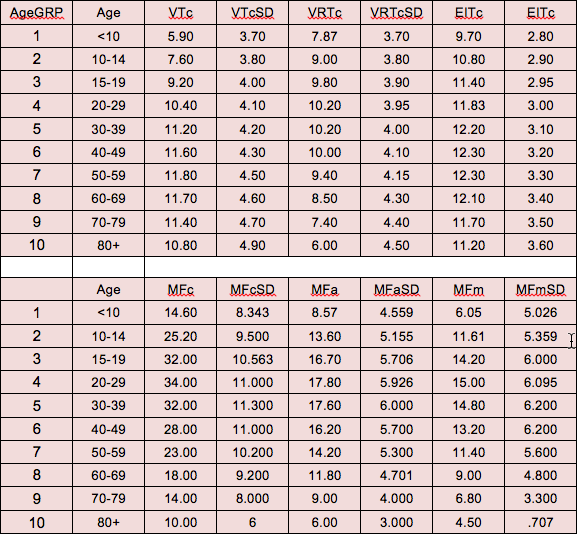
TABLE 9. TGMA NORMS, MEANS AND STANDARD DEVIATIONS
The Vocabulary Test norms increase with age because VT is a measure of “crystallized intelligence.”
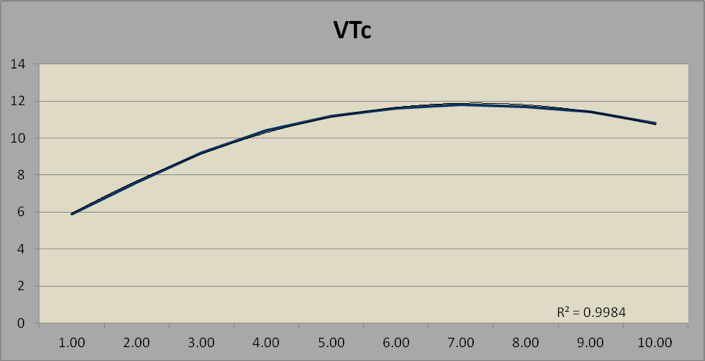
TABLE 3. VOCABULARY TEST
The Visual Reasoning Test declines past age 35 because it is a measure of processing speed or “fluid intelligence.”
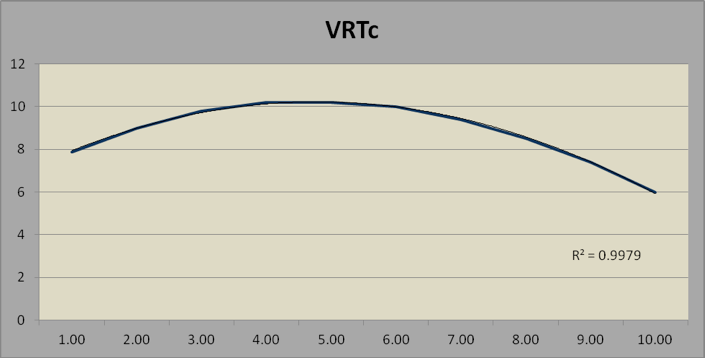
TABLE 4. VISUAL REASONING TEST
The Emotional Intelligence Test has a limited range. It correlates with VT at r = 0.41 and with VRT at r= 0.39.
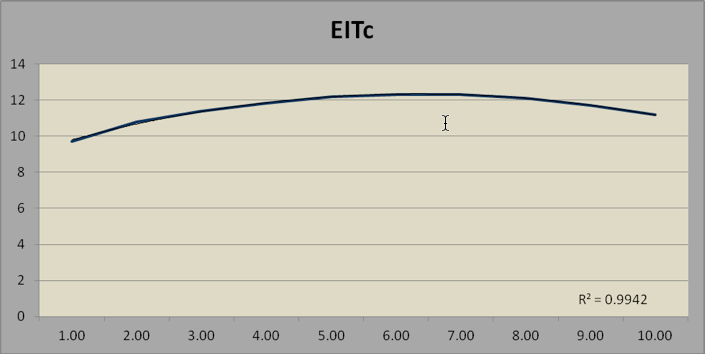
TABLE 5. THE EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE TEST
Math fluency is the sum of MFaddition and MFmultiplication. The three MF parameters relate to age as a third-order polynomial, with linear increase up to age 20, reflecting skill acquisition, and then a quadratic change after age 20, reflecting processing speed.
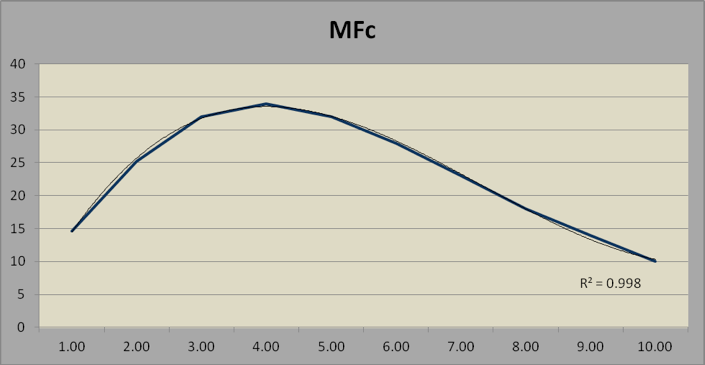
TABLE 6. MATH FLUENCY
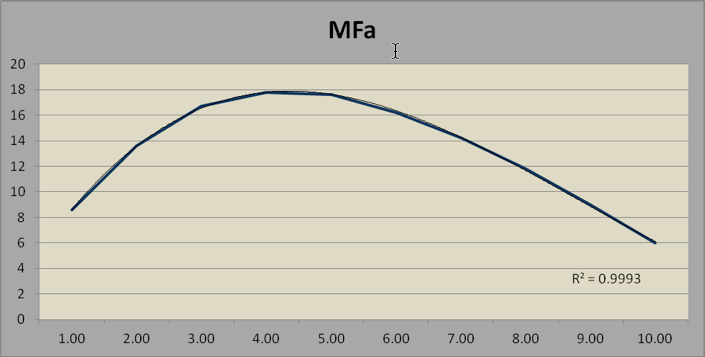
TABLE 7. MATH FLUENCY, ADDITION
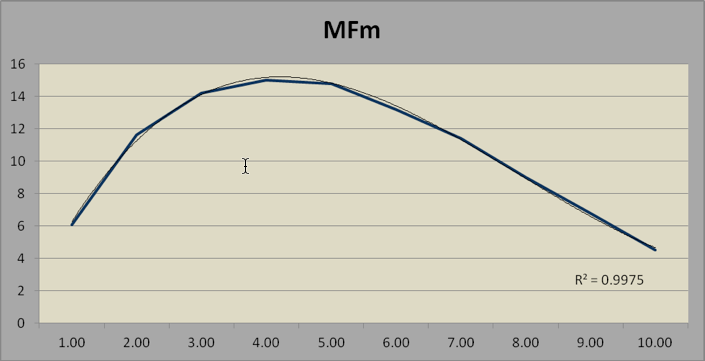
TABLE 8. MATH FLUENCY, MULTIPLICATION
